China has a big dream about One Belt One Road or Belt and Road Initiative. The Chinese people believe that there will be a great resurrection of the Chinese nation if the dream comes true. One Belt One Road is usually called ‘OBOR’ or ‘Belt and Road Initiative”. Through this gigantic project, China wants to link different regions of Asia, Africa and Europe.
For the purpose of funding this project, a bank named Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIT) has been established in China with a capital of one hundred billion dollars. Besides, China has formed forty billion dollar Silk Road Fund. Beijing is using government and non-governmental organizations to implement the plan.
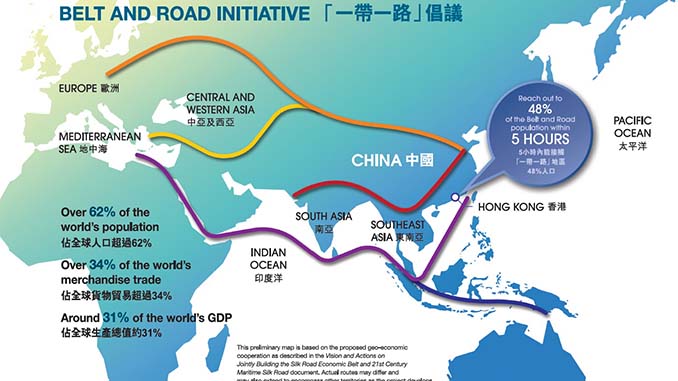
The concept of Belt and Road Initiative is the brainchild of the current Chinese President Xi Jinping. In October 2013, President Xi Jinping presented his visionary plan to the world which is now playing a Key role in redefining China’s relations with the rest of the world. Under the master plan, China wants to connect its mainland with more than sixty countries. The initiative mainly consists of two parts- 1. China will be connected to Central Asia, South and Southeast Asia and Europe by land routes. China is also building oil pipelines along the routes. 2. China will be connected to the Indian Ocean littoral states with waterways. This is the modern version of the ancient Maritime Silk Route.
China is attaching great importance to South and Southeast Asia as part of the One Belt One Road project. The Middle East is also very important to China. Iran is a significant player in China’s Belt and Road initiative. Likewise, Egypt and Israel have vital roles in the BRI. China has already invested $ 4.5 billion in Egypt. China also has a six billion dollar trade agreement with Iran.
The Original Silk Route existed nearly two thousand years ago. It was an important trade route in the world. The route was instrumental for economic, cultural and political exchange between Asia, Africa and Europe. China’s new ‘Silk Road Economic Belt’ and ‘Twenty-First Century Maritime Silk Road’ will also do the same. Business will be expanded with the creation of new and improved infrastructure which will result in economic growth for all countries concerned.
The official map of the “One Belt One Road” shows that there will be a road from China’s Siyan to Urumqi. Beijing will also build a road from China to Spain. The road will go through Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan in Central Asia to Moscow, Poland, Hamburg in Germany, Rotterdam in the Netherlands and finally to Madrid. China is also preparing a master plan for the Maritime Silk Road. Through the Maritime Silk Road, China wants to connect with Sri Lanka, Singapore, Bangladesh and Myanmar in South and Southeast Asia. It will also connect China with Djibouti, Kenya and some other states in Africa.
When the Chinese President Xi Jinping initiated the ‘One Belt One Road’ initiative in 2013, it attracted a lot of attention around the world. It was an attempt to restore the ancient Silk Road which connected the East and the West. Almost sixty countries and several international organizations are involved in this mega project of the twenty-first century. Due to this reason, the project will offer unprecedented opportunities for countries involved. To make the plan a reality, China has initiated a diplomatic offensive across the globe.
In fact, China will construct two ‘Economic Corridors’ under the One Belt One Road. First, there will be a road and a railroad from Kunming to Cox’s Bazar and the second one will be from Kashgar in Xinjiang province of China to Gwadar of Balochistan, Pakistan.
China has a great interest in the One Belt One Road master plan which cannot be denied. But the respective countries can also benefit from the project. Oil pipeline will be added to the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. Transportation of oil in a short time, from the Persian Gulf, will be possible due to the CPEC (China-Pakistan Economic Corridor). China will also get access to the central Asian oil through the CPEC. China is dependent on imported oil. Its reliance on Central Asian oil is increasing due to rapid economic growth and industrialization.
Recommended: Xi Deserves a Third Term
If the CPEC is fully implemented, Pakistan will be able to provide direct employment to seven hundred thousand people. It will increase the economic growth of the country by 2.5 percent. Under the project, highways will be built between Karachi and Lahore. Pakistan’s electricity production will be increased to 10,400 megawatts. The project has already been partially launched. It will link the Gwadar Port of Pakistan to Xinjiang province of China
Even before the One Belt One Road and Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank, China has invested heavily in infrastructure in the region. China has built an oil pipeline in Kazakhstan. It has constructed another pipeline for importing oil from Russia to China.
China also has a plan to connect its Yunnan province. Keeping this in mind, China wants to construct the Kunming-Cox’s Bazar-Kolkata road (which is known as K-to-K). When it is built, Bangladesh will be able to import Chinese goods and products by road. It will save time and money for Bangladesh, China and India to import and export goods and products. Besides, Bangladesh will be able to connect itself with China-Pakistan Economic Corridor. By doing so, Bangladesh will get access to Central Asian oil.
Based on regional cooperation, the BCIM has been formed between Bangladesh, China, India and Myanmar to implement the Belt and Road Initiative in the South Asian region.
Indian Concern Over Belt and Road Initiative
Leaders in New Delhi are concerned about the project. There are three primary reasons for Indian concern and anxiety. First, China’s economic and geopolitical influence in the countries of this region will be increased, if the project becomes successful. Second, under this project, China will invest a huge amount of money in Pakistan, the arch-enemy of India. Third, the Chinese presence in the strategically important Indian Ocean will be increased. As part of this project, China is making large investments in infrastructure and port development in Sri Lanka, Bangladesh and Myanmar. Meanwhile, Sri Lanka’s Port City Development Project has been implemented with 1.4 billion dollars from China. India fears that the Chinese submarines will be stationed in Gwadar Port of Pakistan and Beijing will monitor the Persian Gulf.
Most of the world’s cargo ships use this waterway to transport goods and products to Europe, America and Asia. But China is working to mitigate the fear of India. The Chinese are following a path of fine diplomacy.